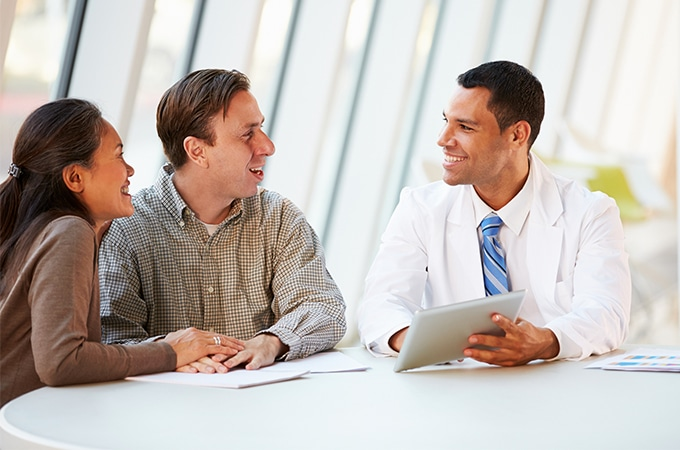
Having a baby through fertility treatments can be a really challenging and tough process when you aren’t guided by the right team of doctors. Any experienced fertility specialist will initially try to educate you about all the options or the line of treatments that you can opt for and also your and your partners’ condition. But there’s something that all of us need to keep in mind; we also need to effectively interact with the fertility specialist to clear all doubts that we have in our minds to be at ease and fully submit or commit to the process.
Be it your pregnancy symptoms or any other complication you face during the whole process, you must discuss it all with your fertility specialist at every step to be sure of your developments all throughout this very delicate journey. Anyway, pregnancy is a very significant journey in any parents’ lives but in this case specifically it becomes way more vital and delicate.
Here’s everything that you must discuss with your fertility specialist at the earliest:
Knowing the primary line of treatment:
Knowing about their own “infertility” can be absolutely devastating to many couples. But the good news is that with advancement in medical science these days it is most likely that you will eventually be able to conceive with intervention, depending on your particular situations. Medications are usually the first-line treatment if your doctor diagnoses you with infertility. These medications are meant to help with increasing the chances of conception and pregnancy. They can come in the form of hormone replacements to stimulate ovulation in women, or medications to treat erectile dysfunction in men. The fertility specialist you go to can also prescribe medicines to increase your chances of staying pregnant once you become pregnant, depending on your reasons for previous miscarriages. In addition, your fertility specialist may recommend lifestyle changes for both partners, such as eating a healthy diet, limiting alcohol consumption, or stopping smoking.
Health impacts before conception:
Indeed fertility can decrease with age, sometimes this is related to health conditions that may develop as you get older. For instance, thyroid conditions in women can affect fertility. Infections, cancer, and poor nutrition can affect both male and female reproductive chances. Also, alcohol consumption, smoking, and certain medications can interfere with fertility. Check on whether your medication list — as well as your partner’s — is compatible with trying to conceive. Most probably, you and your partner will want to be in good health before conception. This not only helps increase the chances of pregnancy, but parental health also directly affects the baby’s health. Scientists recommended that women quit drinking a year before trying for a baby. Your fertility specialist will make specific recommendations to help you get into the best health possible at your medical examination.
Differences between male and female fertility treatments:
In most cases women assume that they are the cause of infertility, but in reality it’s impossible to know without a medical evaluation on both partners. A fertility specialist can determine whether male or female infertility (or both) is keeping you from getting pregnant. Low sperm count or an inability to get or maintain an erection during intercourse can impact fertility in men. In some cases, erectile dysfunction medications help a lot. Lesser sperm count or quality doesn’t mean a pregnancy can’t happen, but it may make it more difficult or it may take longer. Women experiencing infertility can take comfort in the fact that there are multiple options to assist with ovulation difficulties, which is a common culprit of female infertility issues. Some women simply need a boost with ovulating, or ovulating regularly. Your doctor may also prescribe high-dose hormones, such as oestrogen, to help induce ovulation. Other more potent medications come in the form of injections, a process referred to as controlled ovarian hyperstimulation (COH). These may be treated with in-vitro fertilisation (IVF). This process involves fertilising sperm with an egg in a laboratory. Once the fertilisation process is complete, the egg(s) are transferred to your uterus during ovulation. IVF is a good solution for some couples, but it can seem out of reach for others as it can become costly. The main difference between the two procedures is that with IVC, the vagina is used as the incubator for the blastocyst (future baby) for a 5-day period before being transferred to the uterus. The process involves fewer fertility medications than IVF, so it’s an overall comparatively affordable method.
Why do you need surgeries in a fertility treatment?
Your fertility specialist from icareheal might suggest a surgery if they find issues with your reproductive organs. Surgery is sometimes used to repair torn or blocked fallopian tubes so that an egg can be successfully released and fertilised.
Female fertility surgeries may also help treat:
- scars in the reproductive tract
- Uterine fibroids
- Endometriosis
- Polyps
In men, surgical options may be used to repair varicose veins, called varicoceles, in the testicles that can contribute to infertility in some men (though many men with this condition have no trouble with fertility). Surgery is also sometimes used to help open tubes that transfer sperm to the penis.
What are the risks of parents & babies?
While most fertility treatments bear some degree of risk, technology has evolved so that many fertility treatments are now seen as quite safe to the parents and baby-to-be. Surgery might involve risks, such as infection, and fallopian surgery in women can also increase the risk for ectopic pregnancy (a potentially serious condition where an egg and subsequent foetus grows on the outside of your uterus). Clarify with your fertility specialist as many doubts as needed to make sure you are aware of and comfortable with any potential risk before starting a treatment. There’s also a greater chance of premature birth when ART is used for fertility. Premature birth occurs when your baby is born earlier than 37 weeks’ gestation. The risk also increases manifold if you’re pregnant with multiple babies in your womb.